Annuities are insurance products that provide a reliable, steady stream of payments to support your financial needs for the rest of your life or for a predetermined number of years. Because they are contracts, you can also customize them to meet your specific needs and fit your risk tolerance.
Annuities are not for everyone. However, if you’re nearing retirement and need to ensure you can pay your living expenses after you’ve stopped working, an annuity may fulfill those needs.
Key Facts About How Annuities Work
- Annuities work by converting your premium into regular payments that can last for a specified period or your entire life.
- There are many types of annuities, many of which grow your premiums tax-deferred before turning them into income.
- The process of turning the annuity’s value into income is called annuitization.
Annuities can be categorized into different types based on their features. One way to think about annuities is in terms of when the contract is annuitized, or converted into an income stream.
How Do Immediate Annuities Work?
Immediate annuities, as the name suggests, annuitize right after the contract is issued, so owners can receive payments right away.
Steps for How an Immediate Annuity Works
- You purchase the annuity with a single lump-sum payment.
- You can choose when your payments begin, though they must start within 12 months of the contract’s issue date.
- Once your contract annuitizes, you’ll receive regular payments either for a certain number of years or for life, depending on the payout option you choose.
These are the simplest type of annuities, compared to deferred annuities.
How soon are you retiring?
What is your goal for purchasing an annuity?
Select all that apply
How Do Deferred Annuities Work?
Deferred annuities accumulate value on the premium or premiums paid before converting the contract’s value into income payments. These products work differently depending on how the annuity’s value accumulates.
The interest that deferred annuities earn has the advantage of tax deferral. This means you won’t owe any taxes on an annuity’s growth until you receive income from the annuity. In the long run, tax deferral can lead to greater growth because more money is left in the account to compound value.
The tax deferment feature of annuities makes them ideal for high-net-worth individuals, like Ron in this example.
As John Stevenson advises, “When contemplating purchasing an annuity, it’s important to ask what you’re trying to accomplish. If the answer is that you want a fixed rate of returns, guaranteed lifetime income, or the peace of mind of having some of your money in a ‘safe money’ account, then an annuity could be the right choice.”
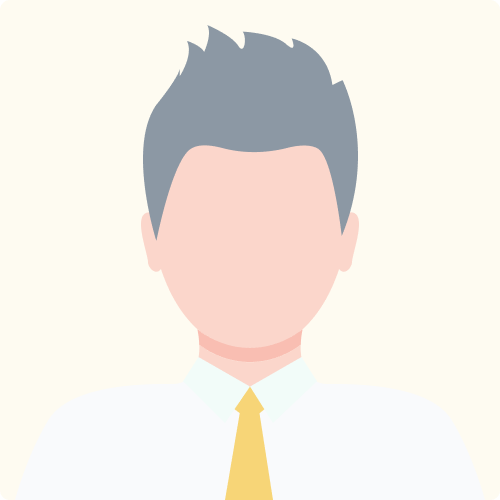

Name: Ron
Age: 55
Income: $180,000/year
- Ron is in good health and nearing retirement
- He has maxed out his 401(k) contributions but still has savings leftover
- Ron wants guaranteed income in retirement that won’t run out
Best Option: Deferred Annuity
Ron’s annuity can earn interest while he’s still working, and he won’t have to pay taxes on that income while he’s still in a higher tax bracket. When the contract annuitizes after Ron retires, he’ll likely be receiving less income and, therefore, could be in a lower tax bracket.
As a result, he’ll end up paying less tax on his annuity earnings than he would on something like a certificate of deposit (CD), which is taxed each year as interest accumulates.
The two most popular types of deferred annuities are fixed annuities and variable annuities.
When a person is contemplating purchasing an annuity, they need to ask themselves what they are trying to accomplish. If the answer is that they want a fixed rate of returns, guaranteed lifetime income or the peace of mind of having some of their money in a “safe money” account, then an annuity could be the right choice.
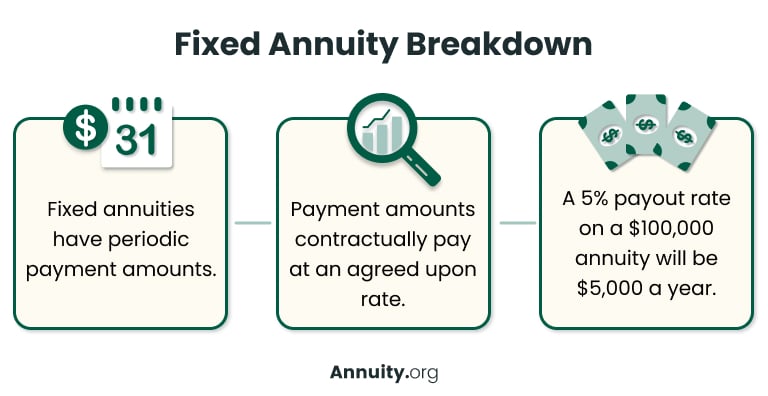
How Do Fixed Annuities Work?
Fixed annuities work very similarly to CDs; you put money into the annuity and let it accumulate interest at a guaranteed rate for a set period. However, unlike a CD, a fixed annuity can be converted into a stream of income as opposed to a lump sum payout once it reaches maturity.
The rate a fixed annuity earns depends on the rates of the low-risk investments and bonds the insurer invests the annuity premiums in.

Overwhelmed by Safe Retirement Options?
Steps of a Fixed Annuity
- You purchase the annuity with either a single lump sum or multiple premium payments.
- The insurance company invests the amount you paid in premiums into low-risk portfolios mainly composed of corporate and government bonds.
- The insurance company collects the growth from its portfolios and credits a portion of that growth as interest to the fixed annuity contract.
- Once the annuity’s surrender period elapses, you can annuitize your contract and begin receiving payments. Only a portion of the payments that represents the interest earned will be considered taxable income.
The most basic version of a fixed deferred annuity is based on a single owner’s life and the payments will end at their death. However, there are additional customizations available to create a contract that fits the owners’ needs.
For instance, it’s possible to include a spouse on the contract, which will make the payments last until both parties have passed away. Additionally, adding a “period certain” or “return of principal” rider to the contract will create a guaranteed return of money for the owners or their heirs regardless of how long they live.
Adding riders like these will lower the monthly payout, so compare your options before committing.
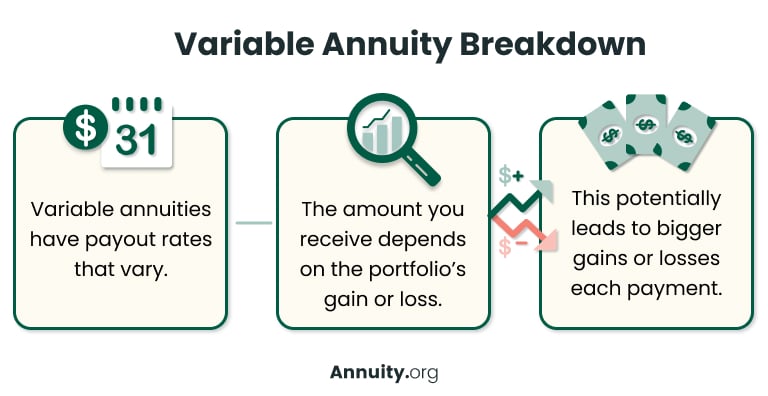
How Do Variable Annuities Work?
Variable annuities are specialized annuities that offer the owners more control over the underlying investments of their contracts. Variable deferred annuities, therefore, may offer higher rates of return when invested more aggressively, but they also require a higher risk tolerance because there are fewer or no guarantees.
Variable deferred annuities do not have a mandatory annuitization requirement and have no limits on the amount that can be contributed over time. One of the biggest benefits of this type of annuity is to supplement the retirement investments for individuals who are already maxing out their other retirement accounts.
Variable deferred annuities typically offer a pre-approved group of mutual funds or ETFs that the investor can invest in. Investment returns are market-based and the contract offers no guarantees on returns.
Because there are no guarantees of the annuity’s value, the income payments from a variable annuity will vary depending on the performance of an investment portfolio. The amount you receive in payments depends on how much money the portfolio gains or loses. This type of annuity is riskier but also has the potential to pay you more in a rising market environment.
It’s important to understand all the costs and rules associated with this type of product before buying it. In a falling market environment, your income payments will not stop, but they will be reduced. The costs associated with this type of product may degrade your ability to recover at the same rate as the market.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Annuities Work
The type of annuity you purchase and the terms of your contract dictate exactly how you’ll be paid from your annuity. You typically receive the principal back from an annuity in the form of periodic annuity payouts.
An annuity is a financial product structured by a long-term contract between you and an insurance company. Annuities are part of a retirement strategy designed to provide you with a steady stream of guaranteed income in retirement.
Market fluctuations have different effects on different types of annuities. Fixed annuities, for example, guarantee your returns no matter how the market performs. Other types, like variable annuities, carry more risk in down markets because their value is tied to the performance of underlying investments.