A retirement annuity is an option for Americans looking to ensure a secure and stable income stream when they retire. Annuities have become an increasingly popular retirement planning resource as pension plans have become more and more rare in the private sector.
Key Facts About a Retirement Annuity
- A retirement annuity is an insurance contract that allows individuals to set aside money to pay themselves a steady income during retirement, providing financial stability in their later years.
- There are three primary types of retirement annuities: fixed, variable, and indexed, each offering different features and benefits to suit various financial goals and risk tolerances.
- Purchasing a retirement annuity can be done through a lump-sum payment or a series of payments over time, typically years before retirement, allowing for the accumulation of funds to support future income needs.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, only 15% of private industry workers had access to any kind of employer-provided pension, known as a defined benefit plan, as of November 2021. Pensions, like retirement annuities, guarantee a steady income after retirement.
At the same time, workers are being provided more options to save money for their retirements. Just over four-fifths — 81% — of private sector employees had access to employer-provided retirement plans such as 401(k) plans, in 2021.
But retirement plans provide only savings — they do not provide guaranteed retirement income. That is where a retirement annuity comes into play as an invaluable aspect of your overall retirement plan.
How soon are you retiring?
What is your goal for purchasing an annuity?
Select all that apply
What Is a Retirement Annuity and How Does It Work?
A retirement annuity is an insurance contract that allows you to set aside money to pay yourself an income in retirement. The income is paid out on a schedule — usually monthly, quarterly or annually — giving you the peace of mind that you have a steady income stream to rely upon during your golden years.
The money you use to purchase a retirement annuity is called the premium. You typically purchase a retirement annuity years before retirement and pay the premium either with a lump-sum payment or with a series of payments over time.
There are three primary types of retirement annuities: fixed, variable and indexed.
- Fixed Annuities
- A fixed annuity provides a fixed amount of return, or income, over a specific number of years or over your lifetime. With a fixed annuity, you will know ahead of time how much return to expect when the payments start.
- Variable Annuities
- A variable annuity offers more opportunities to grow your money in the annuity before you retire, but also comes with more risk. You are able to select subaccounts — a variety of stocks and bonds — in which to invest your premium. Your eventual payout is based upon how well your investments in the market perform, and therefore, is less predictable than the return of a fixed annuity.
- Fixed Index Annuities
- A fixed index annuity offers growth, safety and enough access to allow annual withdrawals. This type of annuity is tied to a stock index, such as the S&P 500. Index-linked interest, along with tax deferral, help your money grow. And if the index performs poorly, an index annuity retains its values and loses nothing.
Fixed vs. Variable vs. Fixed Index Annuities
Read More: Is One Million Dollars Enough To Retire?
How Does a Retirement Annuity Pay Out?
Retirement annuities generate income based on the way they pay out. There are two types of payouts available with a retirement annuity: immediate or deferred. The names reflect when the payout begins.
Immediate Annuities
Some buyers choose to put a portion of their savings toward an immediate annuity as a lump-sum payment right before they retire. Immediate annuities require an upfront, one-time premium.
Once you’ve paid the premium, the payout begins in monthly installments. Usually the payout begins in less than a year depending on the terms of your annuity.
This option is best suited for people close to retirement age looking to use a portion of their nest egg to ensure steady payments throughout retirement.
Deferred Annuities
Deferred annuities, on the other hand, can be built over several years. You pay your premium — often in smaller payments over time — but don’t start collecting your payout until some point in the future after you retire. This allows your money to grow, either as interest if you have a fixed or fixed index annuity or with stock and bond market gains if you have a variable annuity.

Worried About Your Retirement Savings?
Why Is a Retirement Annuity Important?
The decimation of pensions has left most of a huge generation facing retirement feeling unequipped and unprepared. In fact, research by Consumer Affairs shows that 63% of baby boomers believe they will have to keep working to make extra income in retirement.
“Americans are living longer and face a variety of risks in retirement,” Michael Finke, a research fellow and dean and chief academic officer of the American College of Financial Services, said in a 2018 news release announcing the Protected Lifetime Income Index research initiative.
Most retirees today rely on withdrawals from their retirement savings — IRAs, 401(k) plans or similar defined contribution plans — to pay for expenses in retirement, according to Finke.
“If they had an annuity to accompany their savings and investments, [retirees] could always count on a source of guaranteed monthly income, which would reduce the risk of running out of money. And annuities are a solution that can provide that protected income for life,” Finke said.
In fact, various studies have found that retirees with guaranteed income in addition to Social Security are more likely to report being happy.
“Annuities are a solution that can provide that protected income for life.”
Dr. Michael Finke, American College of Financial Services
Seventy-one percent of investors between the ages of 45 and 54 expressed interest in purchasing an annuity as part of their retirement income plan, according to a 2021 survey by the Alliance for Lifetime Income.
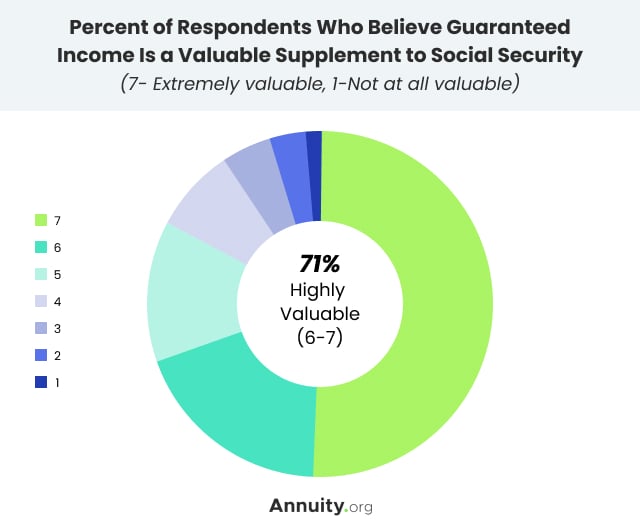
The survey questioned 1,519 people between 45 and 75 years old with $100,000 or more in household assets. Roughly a third of the survey respondents were partially or fully retired.

Learn how an investment today can provide guaranteed income for life.
How Can You Use Retirement Annuity Income?
People use income from their retirement annuities in several different ways. How you choose to use it should reflect your retirement goals and needs.
- Pay for Retirement Goals
- You can budget your retirement annuity income toward hobbies, travel and other costs associated with any retirement goals you have planned.
- Cover Fixed Expenses
- Coupled with Social Security, annuity income can be used to cover fixed expenses — rent, mortgage, utilities — that you had used your paycheck to cover before retirement.
- Reduce Your Urge to Splurge
- Building a retirement budget around a stream of income — annuity payouts and Social Security — keeps you from overspending.
Ways to Use Retirement Annuity Income
The overarching advantage of retirement annuity income in these circumstances is that it can be used to protect your retirement savings for other expenses that inevitably pop up.
Read More: How Do Annuities Affect Social Security Retirement Benefits?
I had someone reach out to me last month who wanted the highest lifetime payout possible and after showing the SPIA/DIA as well as income rider options, he decided to go with the income rider option because the lifetime annual payout was higher than any other option. This is usually the best option for people who want the highest income. Other people I’ve helped did not need the income, only the growth. In these instances, I show them growth FIA and MYGA annuities that focus on growth and legacy rather than income.
Where Does an Annuity Fit Into Your Retirement Plan?
A retirement annuity can be a key part of your overall retirement strategy. It can be coupled with other more traditional financial tools of retirement planning — IRAs, 401(k) plans, life insurance, etc. — to create a well-rounded retirement plan.
An annuity can also be a form of paycheck replacement during retirement. The payout provides a steady, scheduled income that you will keep receiving for as long as you live.
You can think of a retirement annuity as the mirror image of traditional life insurance policies. Life insurance provides protection for your loved ones in the event of your premature death. Annuities provide income for you, insuring you against outliving your retirement savings.
By buying an annuity, you can diversify your retirement portfolio, giving you more financial flexibility in retirement.