A key component of comparing and evaluating the purchase of an annuity or reviewing the value of an annuity you already own is the present value calculation. The critical assumption of present value is that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future. When comparing or evaluating annuities, present value is a way to place two or more different products on an equal standing and compare their present discounted values.
Key Facts About an Annuity Table
- An annuity table helps compare different annuities by calculating present value without complex formulas.
- Understanding terms like PVIFA, term, period, interest rate, and principal is essential for accurate annuity calculations.
- A dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future due to inflation and utility, impacting annuity evaluations.
Before diving into the annuity table explanation or calculations, let’s walk through the important terminology.
Annuity Terminology
- Present Value Interest Factor of an Annuity (PVIFA): The figure used to calculate the present value of a series of regular uniform annuity payments. Multiplying the annuity payment by the present value factor equals the present value.
- Term: The length of time the annuity is guaranteed to pay a given rate of return or payment. For fixed products, it is also referred to as maturity.
- Period: The length of time between payments within a given year. A monthly annuity has 12 periods. Over the course of a five-year annuity term, a monthly annuity will have 60 periods.
- Interest Rate: The rate of return offered by the annuity policy.
- Principal: The contribution(s) supplied by the contract owner to fund their annuity. For tax purposes, this is considered tax basis, and its return as income payments is not taxable.
What Is an Annuity Table?
An annuity table is a simple tool that provides an easy way to determine the current present value of your annuity. A table allows you to skip the more complicated calculations necessary to determine the present value. Think of it as a cheat sheet.
“These tables provide factors that are applied directly to the annuity payment amount and eliminate the need for complex calculations,” according to Alec Kellzi, CPA at IRS Extension Online.
To solve for the present value of your policy, you will multiply your annuity’s monthly payment by the assigned value on the table. This value, called the present value interest factor of an annuity (PVIFA), is a multiplier determined by the annuity interest rate and the number of remaining payments. Below, you’ll find an example, step by step, of how to do this.
One of the biggest benefits of using an annuity table is standardizing your methods for assigning and comparing value for annuities, regardless of their amounts, interest rates or terms. The IRS uses this same method for its calculations when annuities must be valued for tax purposes.
The present value of an annuity is the current value of all future payments you will receive from the annuity. This comparison of money now and money later underscores a core tenet of finance – the time value of money. Essentially, in normal interest rate environments, a dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow because it has the ability to earn interest and grow with time.
How soon are you retiring?
What is your goal for purchasing an annuity?
Select all that apply
How To Use Annuity Table Data
For the annuity table to be useful, you must begin with basic knowledge of your payment details. To start, find out the exact timing of your payments. Any product that pays out at the end of a period is considered an ordinary annuity. This applies to stock dividends, bond coupons and annuity contracts. This is the most common type of annuity payment structure.
When payments come at the beginning of the period, such as rental income from an investment property, they are referred to as an annuity due. Conversely, annuity contracts do not operate this way.
You’ll need to use a different table depending on which one you are calculating.
- 1. Confirm the timing of your payments
- They will be received at the beginning or the end of each period. Choose the corresponding present value table.
- 2. Identify the interest rate and the number of periods
- This information can be found in your annuity contract.
- 3. Find the present value interest factor of an annuity (PVIFA)
- This number will be the intersection point of your interest rate and your number of remaining payments. Interest rates will be on one axis, and the number of remaining payments will be on the other axis.
- 4. Calculate the present value
- Once you have the present value factor, multiply it by the amount of each payment in your annuity. The result is the present value of your annuity.
Step-by-Step: Using an Annuity Table to Calculate the Present Value
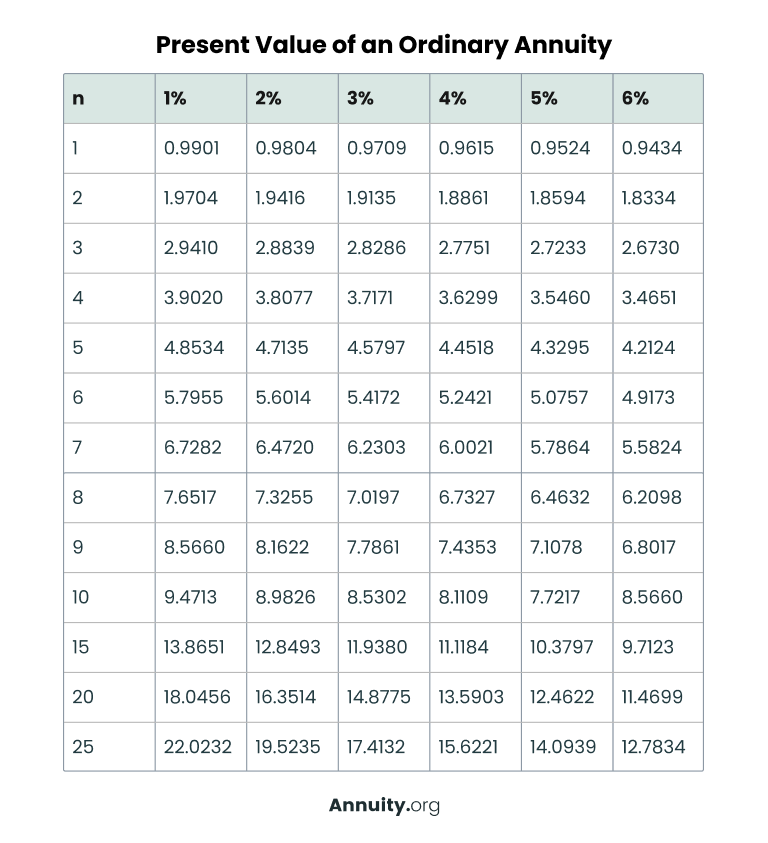
Annuity Table for Ordinary Annuities
| Interest Rate (r) | ||||||
| Number of Payments (n) | 1% | 2% | 3% | 4% | 5% | 6% |
| 1 | 0.9901 | 0.9804 | 0.9709 | 0.9615 | 0.9524 | 0.9434 |
| 2 | 1.9704 | 1.9416 | 1.9135 | 1.8861 | 1.8594 | 1.8334 |
| 3 | 2.941 | 2.8839 | 2.8286 | 2.7751 | 2.7233 | 2.673 |
| 4 | 3.902 | 3.8077 | 3.7171 | 3.6299 | 3.546 | 3.4651 |
| 5 | 4.8534 | 4.7135 | 4.5797 | 4.4518 | 4.3295 | 4.2124 |
| 6 | 5.7955 | 5.6014 | 5.4172 | 5.2421 | 5.0757 | 4.9173 |
| 7 | 6.7282 | 6.472 | 6.2303 | 6.0021 | 5.7864 | 5.5824 |
| 8 | 7.6517 | 7.3255 | 7.0197 | 6.7327 | 6.4632 | 6.2098 |
| 9 | 8.566 | 8.1622 | 7.7861 | 7.4353 | 7.1078 | 6.8017 |
| 10 | 9.4713 | 8.9826 | 8.5302 | 8.1109 | 7.7217 | 7.3601 |
| 15 | 13.8651 | 12.8493 | 11.938 | 11.1184 | 10.3797 | 9.7123 |
| 20 | 18.0456 | 16.3514 | 14.8775 | 13.5903 | 12.4622 | 11.4699 |
| 25 | 22.0232 | 19.5235 | 17.4132 | 15.6221 | 14.0939 | 12.7834 |
Annuity Table for Annuity Due
| Interest Rate (r) | ||||||
| Number of Payments (n) | 1% | 2% | 3% | 4% | 5% | 6% |
| 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 1.9901 | 1.9804 | 1.9709 | 1.9615 | 1.9524 | 1.9434 |
| 3 | 2.9704 | 2.9416 | 2.9135 | 2.8861 | 2.8594 | 2.8334 |
| 4 | 3.941 | 3.8839 | 3.8286 | 3.7751 | 3.7232 | 3.673 |
| 5 | 4.902 | 4.8077 | 4.7171 | 4.6299 | 4.546 | 4.4651 |
| 6 | 5.8534 | 5.7135 | 5.5797 | 5.4518 | 5.3295 | 5.2124 |
| 7 | 6.7955 | 6.6014 | 6.4172 | 6.2421 | 6.0757 | 5.9173 |
| 8 | 7.7282 | 7.472 | 7.2303 | 7.0021 | 6.7864 | 6.5824 |
| 9 | 8.6517 | 8.3255 | 8.0197 | 7.7327 | 7.4632 | 7.2098 |
| 10 | 9.566 | 9.1622 | 8.7861 | 8.4353 | 8.1078 | 7.8017 |
| 15 | 14.0037 | 13.1062 | 12.2961 | 11.5631 | 10.8986 | 10.295 |
| 20 | 18.226 | 16.6785 | 15.3238 | 14.1339 | 13.0853 | 12.1581 |
| 25 | 22.2434 | 19.9139 | 17.9355 | 16.247 | 14.7986 | 13.5504 |
Time Value of Money
The concept of the time value of money could be explained most simply by the phrase, a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future.
Inflation is one component of this idea, given that over time inflation eats away at the purchasing power of the dollar. The same dollar will be able to buy less 10 years from now than it could buy today.
Utility is another factor. Most people would like to use a dollar today more than a dollar in 10 years regardless of whether the purchasing power is exactly the same.
Together these two components bias us towards wanting to use money now. In order to offset the utility and inflation risk, an investor must be adequately compensated through a positive rate of return for stashing away money for later.
Present value helps to level the playing field for comparing different options and investments so that we can determine which may offer the best balance of total value, growth and safety.

Overwhelmed by Safe Retirement Options?
Math Alert: Using the Present Value Formula (Ordinary Annuity)
While an annuity table provides a quick and easy way to calculate the present value of an annuity, it’s not the only method. Another approach is to use the present value formula. This mathematical equation, while more complex, is more precise.
Present Value Formula Components
- P = Present Value Result
- PMT = Period Payment (monthly, quarterly, annually)
- r = Interest rate
- n = Number of remaining periods
Both of the versions of the formula below are interchangeable to calculate the present value of an ordinary annuity and will yield the same result. To compare the results of the annuity table vs. the formula, the present value factor of the annuity table is meant to replace the entire fraction portion of the equation to the right of the multiplication sign.
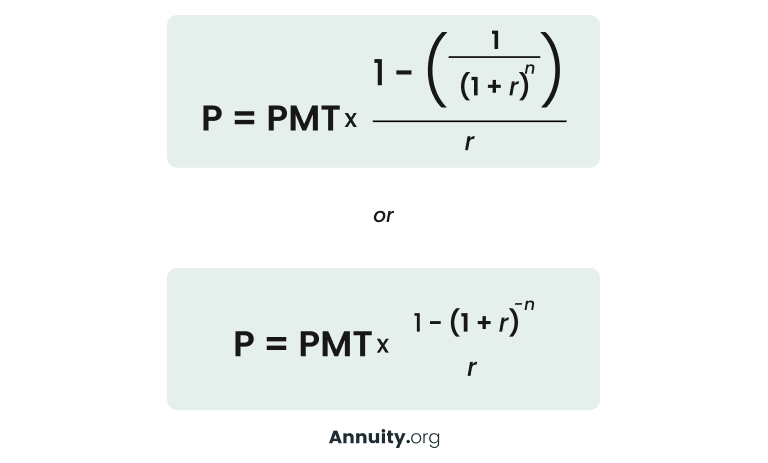
Other Methods for Calculating the Present Value of an Annuity
For those who like to do it themselves, you can break down the formula into its individual components and build your own present value calculator in a spreadsheet, or you can use our fixed annuity calculator to save time.
Note: The calculator calculates present value based on the assumption that payments are received at the end of each period, as is most common with ordinary annuity contracts. For the formula for calculating the present value of an annuity due, please review our FAQs below.
Frequently Asked Questions About Annuity Tables
The annuity due formula is similar to the ordinary annuity formula but includes an additional factor to incorporate the earlier payment timing.
Calculating the present value of an annuity can help you determine whether taking a lump sum or opting for future annuity payments spread out over many years will be more beneficial to your financial needs or goals. It can be a helpful exercise to compare comparable products with different benefits or riders.
Annuity tables are visual tools that help make the otherwise complex mathematical formula of present value much easier to calculate. They compute the predetermined numbers of periodic payments against various annuity rates in a table format. You cross reference the rows and columns to find your annuity’s present value.